HPA Axis Hormone Profiling
Supports studies of hormone regulation under stress or metabolic load by monitoring key upstream and downstream changes in adrenal-related pathways.
Steroid hormones are lipophilic messengers derived from cholesterol. They include glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. These molecules diffuse across membranes and bind nuclear or membrane receptors. Receptor binding regulates transcription, signaling, and downstream metabolism.
Production occurs mainly in adrenal tissue and gonads. Circulating steroids exist as free molecules or protein-bound pools. Phase I and phase II enzymes convert them to active, inactive, or conjugated forms. Sulfates and glucuronides extend half-life and change polarity, shaping excretion and detection.
Small structural changes create large functional differences. One hydroxyl group can alter receptor affinity and bioactivity. This is why steroid hormone analysis favors LC–MS/MS profiling. The method distinguishes isomers, resolves isobars, and quantifies low-abundance targets.
In research and development, steroid pathways inform mechanism and safety. You can track stress response, fluid balance, and reproductive endpoints. Panels covering precursors, actives, and metabolites reveal pathway bottlenecks and enzyme shifts. Measuring free and conjugated pools clarifies exposure, clearance, and tissue dynamics.
Detailed, Customizable, and Pathway-Driven Sterol Profiling
HPA Axis Hormone Profiling
Supports studies of hormone regulation under stress or metabolic load by monitoring key upstream and downstream changes in adrenal-related pathways.
Androgen Pathway Assessment
Covers major androgens and their related biosynthetic steps to help clarify shifts in hormone levels across physiological or experimental conditions.
Estrogen Metabolism Analysis
Profiles parent estrogens alongside downstream metabolic routes to support comparative studies across sexes, timepoints, or treatment responses.
Free vs Conjugated Hormone Evaluation
Offers selective measurement of free hormones, intact conjugates, or total pools, depending on how exposure or metabolic clearance needs to be interpreted.
Neuroactive Steroid Panel
Designed for brain- or neural-related studies, this panel targets compounds relevant to neurological and behavioral research, with appropriate sample handling options.
Adrenal Steroid Mapping
Targets a broader range of steroid precursors and intermediates involved in adrenal function, offering more complete context for pathway interpretation.
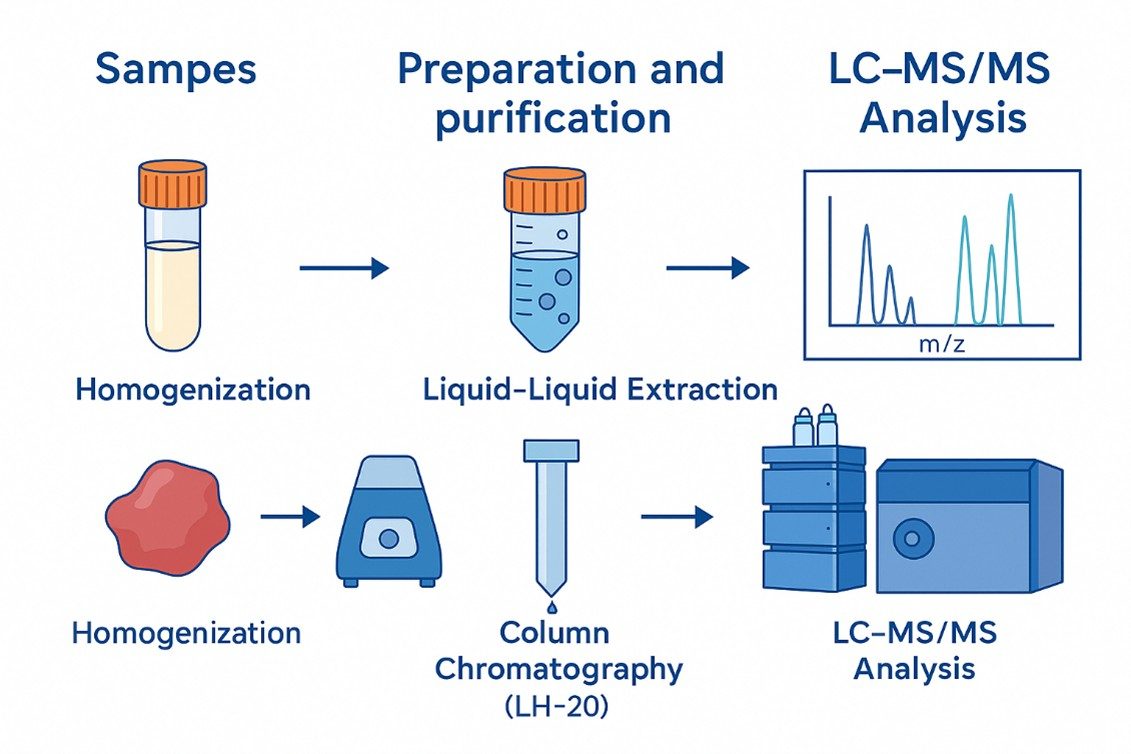
Below is a representative scope of targets for steroid hormone analysis and LC–MS/MS steroid profiling. Items can be measured as free compounds, intact conjugates, or after controlled hydrolysis, depending on study goals.
| Class / Pathway | Representative Analytes (Free) | Conjugates & Related Derivatives |
|---|---|---|
| Glucocorticoids & C21 Precursors | Cortisol, Cortisone, Corticosterone, 11-Deoxycortisol, 21-Deoxycortisol, 17-Hydroxyprogesterone, Progesterone, 17-Hydroxypregnenolone, Pregnenolone, Allopregnanolone | Cortisol Sulfate/Glucuronide, Cortisone Sulfate/Glucuronide, THF, Allo-THF, THE |
| Mineralocorticoids | Aldosterone, 11-Deoxycorticosterone | Aldosterone-18-Glucuronide (where applicable) |
| C19 Androgens | Testosterone, Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), Androstenedione, Androsterone, Etiocholanolone, 3α-/3β-Androstanediol | Testosterone Sulfate/Glucuronide, DHT Sulfate/Glucuronide |
| 11-Oxygenated Androgens | 11β-Hydroxyandrostenedione, 11-Ketoandrostenedione, 11β-Hydroxytestosterone, 11-Ketotestosterone | Corresponding sulfates/glucuronides |
| Estrogens (C18) | Estrone (E1), Estradiol (E2), Estriol (E3), 2-/4-Hydroxyestrone, 2-/4-Hydroxyestradiol, 2-/4-Methoxyestrogens | E1/E2/E3 Sulfates/Glucuronides, Catechol/Methoxy conjugates |
| Adrenal Steroids (Δ5 pathway) | DHEA, 7-Hydroxy-DHEA, 7-Oxo-DHEA | DHEA-S and other sulfates |
| Neurosteroids | Allopregnanolone, Pregnanolone, Tetrahydroprogesterone species | Sulfate/Glucuronide forms where applicable |
| Phase I Metabolites | 5α-/5β-Reduced steroids, 16α-/16β-Hydroxylated species | Conjugated counterparts (sulfates/glucuronides) |
| Method Controls (Surrogates/IS) | Isotope-labeled analogs covering each class | — |

SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ (Figure from Sciex)

TSQ Altis Triple Quadrupole MS (Figure from Thermo Scientific)

Orbitrap Exploris 480 (Figure from Thermo Fisher)
Quantitative Results Table
Chromatograms & Spectra
Calibration & Linearity Summary
LOD/LOQ (Matrix-Matched)
Explore our Lipidomics Solutions brochure to learn more about our comprehensive lipidomics analysis platform.

Endocrine Research
Tracks hormone biosynthesis and conversion rates to understand regulatory pathways and enzyme kinetics.
Reproductive Biology
Quantifies androgen and estrogen profiles to study hormone regulation in gametogenesis and developmental processes.
Pharmacology & Drug Metabolism
Evaluates drug–hormone interactions, metabolic stability, and pathway modulation in preclinical models.
Environmental and Ecotoxicology Research
Detects steroid-like compounds and endocrine-active substances in environmental or biological samples.
Stress and Metabolic Studies
Monitors adrenal responses and steroid balance under nutritional, environmental, or physiological stress.
Translational & Systems Biology
Integrates steroid data with transcriptomics or metabolomics to reveal network-level regulation and pathway crosstalk.
| Sample Type | Recommended Volume / Amount | Container | Preservatives / Additives | Storage Conditions | Shipping Instructions | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum / Plasma | ≥ 200 µL (preferably 300 µL) | 1.5 mL low-bind microtube or cryovial | None; avoid heparin and EDTA when possible | Store at −80 °C; avoid repeated freeze–thaw | Ship on dry ice in secondary sealed bag | Record anticoagulant if used; avoid hemolysis and lipemia |
| Urine | ≥ 1 mL | Sterile polypropylene tube | Optional: pH ≈ 6–7 buffer if extended storage | Store at −20 °C or below | Ship frozen with ice packs or dry ice | Mix thoroughly; note collection time and dilution factor |
| Tissue (fresh or frozen) | 30–50 mg wet weight | Cryovial, RNase/DNase-free | None | Snap-freeze in liquid N₂; store at −80 °C | Ship on dry ice; label species + tissue type | Record tissue source and region; avoid fixatives |
| Cell Pellet | ≥ 1 × 106 cells | Cryovial | None | Store at −80 °C immediately after centrifugation | Ship on dry ice | Wash twice with PBS; remove medium residues |
| Cell Lysate / Extract | ≥ 100 µL | Low-bind microtube | Keep buffer MS-compatible; avoid detergents, glycerol > 5%, or > 200 mM salt | Store at −80 °C | Ship on dry ice | Include buffer composition; note protein concentration if available |
| Culture Medium / Supernatant | ≥ 500 µL | Sterile polypropylene tube | None | Store at −20 °C or below | Ship frozen | Filter or centrifuge to remove cells/debris |
| Saliva (research only) | ≥ 500 µL | Salivette or polypropylene tube | None | Store at −20 °C | Ship frozen | Collect unstimulated samples; avoid food, caffeine, and nicotine 1 h before collection |
General Guidelines:
What is the most accurate way to measure steroid hormones?
Targeted LC–MS/MS is widely regarded as the reference approach because it separates isomers, minimizes cross-reactivity, supports multiplex panels, and delivers high specificity at low concentrations. These advantages are emphasized in endocrine best-practice reviews and method papers.
Can multiple steroid hormones be quantified in one run?
Yes. LC–MS/MS enables multiplexed panels that quantify many steroids simultaneously, improving throughput and comparability across samples while maintaining selectivity.
Do you measure free and conjugated forms separately?
We can measure free hormones, intact conjugates (sulfates/glucuronides), or total pools after controlled hydrolysis; this is a common LC–MS/MS strategy used to interpret biosynthesis and clearance.
How is data accuracy maintained across batches and labs?
Accuracy and comparability rely on matrix-matched calibration, isotope-labeled internal standards, QC samples, and participation in recognized standardization frameworks (e.g., CDC hormone standardization and reference procedures).
What are the main challenges in steroid testing, and how are they handled?
Typical issues include matrix effects, isobaric overlap, and isomer separation. Optimized extraction/SPE, chromatographic resolution, qualifier-ion ratios, and—when needed—PRM or orthogonal methods address these challenges.
Is LC–MS/MS better than immunoassay for low-level steroids?
For low concentrations and isomeric interferences, LC–MS/MS generally shows higher specificity and accuracy than immunoassays; consensus statements recommend standardization to ensure reliable results.
Are saliva measurements reliable for research use?
Validated LC–MS/MS methods can establish saliva reference ranges and quantify multiple steroids with appropriate sensitivity, offering a convenient, non-invasive matrix when matched to study goals.
Why do some labs emphasize participation in standardization programs?
External standardization and reference measurement procedures reduce between-laboratory bias and improve long-term comparability of steroid data—important for multi-site or longitudinal research.
How do you confirm selectivity when isomers co-elute?
We combine chromatographic separation with multiple qualifier transitions and retention-time criteria; if necessary, high-resolution PRM or GC–MS/MS confirmation is applied to verify identity.
Can results integrate with other omics analyses?
Yes. Quantitative steroid panels measured by LC–MS/MS are frequently integrated with transcriptomics or metabolomics to contextualize enzyme activity and pathway crosstalk. (General LC–MS multiplexing and pathway applications support this integration.)
What influences the choice of matrix (serum vs urine vs saliva)?
Decision factors include target concentration range, conjugation state, and study design. Serum/plasma support broad panels; urine is useful for excreted metabolites; saliva offers non-invasive sampling of bioavailable fractions when methods are validated.
What about standardization for testosterone and estradiol in particular?
CDC programs provide reference procedures and standardization materials to verify calibration and improve trueness for these high-impact analytes.

Services:
Resource:
Platform:
Online Inquiry
CONTACT US