Targeted quant panels (core eicosanoids)
A focused panel for eicosanoid pathway profiling across COX/LOX/CYP outputs. It fits inhibitor studies, perturbation screens, and time-course designs.
Our services have earned the trust of companies, schools, and organizations globally, and we remain dedicated to maintaining that trust.
Eicosanoids are potent lipid signals made from polyunsaturated fatty acids. They include prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, lipoxins, and many hydroxylated or epoxidized products.
Teams measure them as direct pathway readouts. They can shift quickly after stimulation, treatment, or stress. They also appear at low levels in many matrices.
Eicosanoid quantification is challenging because:
Targeted quant panels (core eicosanoids)
A focused panel for eicosanoid pathway profiling across COX/LOX/CYP outputs. It fits inhibitor studies, perturbation screens, and time-course designs.
Expanded eicosanoid coverage (metabolites and pathway branches)
Adds commonly requested downstream metabolites and pathway branch markers when they are feasible in your matrix.
Custom targets and add-on pathways
Add specific analytes tied to your mechanism or model, subject to standard availability and chromatographic feasibility.
Absolute quantification (isotope dilution, optional)
Stable isotope–labeled internal standards and calibration curves can be applied to report absolute concentrations for targets with suitable standards and validated transitions.
If your study extends beyond arachidonic acid–derived eicosanoids—such as DHA/EPA lipid mediators—or you need broader pathway coverage, see our Oxylipin Quantification and Pathway Profiling for expanded panels, including specialized pro-resolving mediators and other oxidized PUFA products.
| Subgroup | Analytes |
|---|---|
| Series prostaglandins | PGE2, PGD2, PGF2α, PGE1, PGD1, PGF1α, PGE3, PGD3, PGF3α |
| Prostacyclin pathway markers | 6-keto-PGF1α, 6-keto-PGE1 |
| Dehydration / cyclopentenones | PGA2, PGB2, PGJ2, 15-deoxy-PGJ2, 15-deoxy-PGD2, 15-deoxy-PGA2 |
| Oxidation / breakdown markers | 15-keto-PGE2, 15-keto-PGD2, 15-keto-PGF2α, 15-keto-PGF1α, PGEM, PGFM, bicyclo-PGE2 |
| Hydroxy derivatives | 11β-PGF2α, 11β-PGE2, 19-hydroxy-PGE2, 20-hydroxy-PGE2 |
| Subgroup | Analytes |
|---|---|
| Thromboxane readouts | TXB2, TXB1, TXB3 |
| Subgroup | Analytes |
|---|---|
| Leukotriene series | LTB4, 20-hydroxy-LTB4, 20-carboxy-LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 |
| Hydroxy and oxo products | 5-HETE, 12-HETE, 15-HETE, 20-HETE, 11-HETE, 5-oxo-ETE |
| Subgroup | Analytes |
|---|---|
| Lipoxins | LXA4, LXB4 |
| Subgroup | Analytes |
|---|---|
| Epoxides | 8,9-EET, 11,12-EET, 14,15-EET |
| Subgroup | Analytes |
|---|---|
| Pathway substrate | Arachidonic acid |
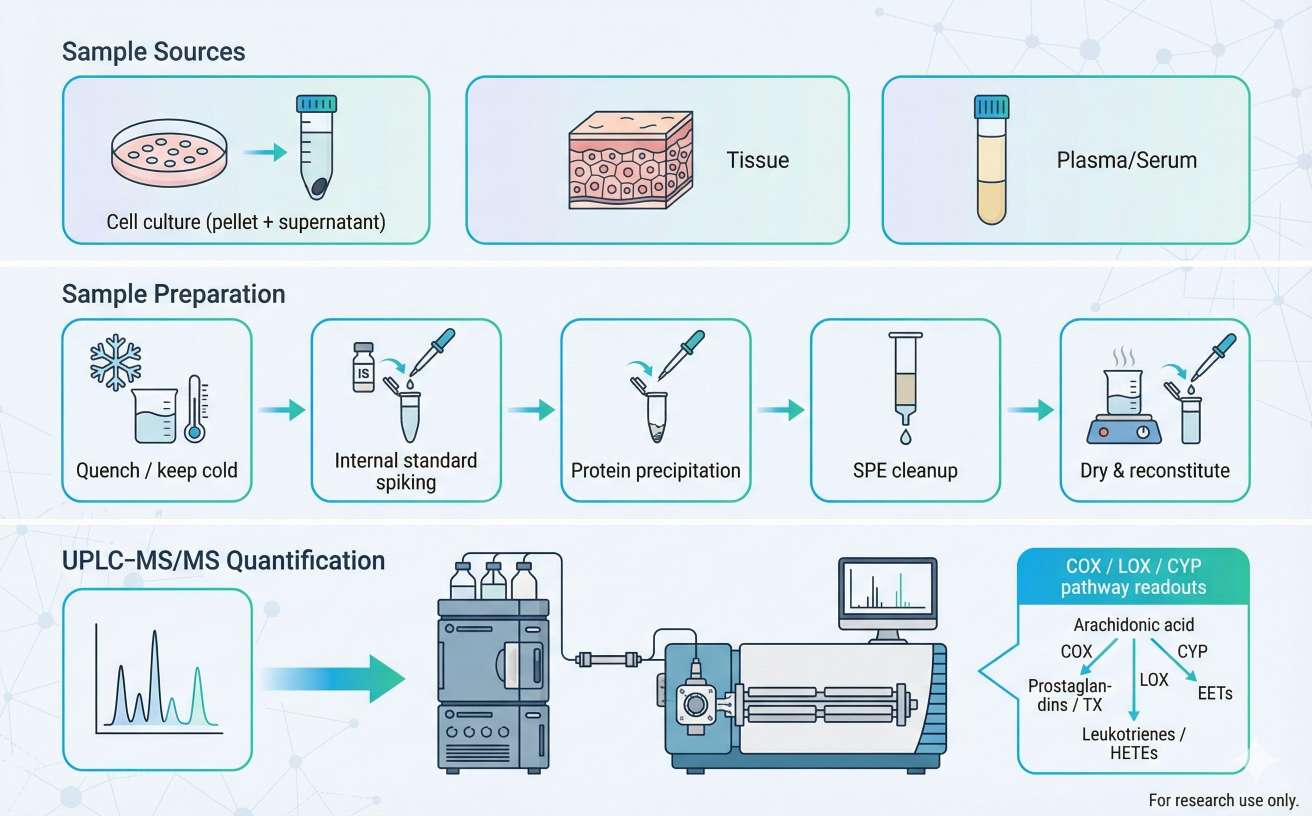
Eicosanoids are low-abundance lipid mediators with many structural isomers. To support confident quantification in research matrices, we use targeted UPLC–MS/MS (scheduled MRM) on a triple quadrupole–class platform.
| Component | Model | Purpose in eicosanoid quantification |
|---|---|---|
| UPLC | Waters ACQUITY UPLC | Fast, stable separations to support isomer handling and reproducible retention time |
| MS/MS | SCIEX QTRAP 6500 | Targeted MRM quantification with high selectivity for low-level lipid mediators |
| Ion source | Turbo V ESI (QTRAP 6500 source) | Stable ionization for acidic eicosanoids in complex matrices |
We tune chromatography to separate closely related mediators and reduce interference.
| Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Column | ACQUITY UPLC BEH Shield RP18, 2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm |
| Column temperature | 40 °C |
| Flow rate | 0.5 mL/min |
| Injection volume | 10 μL |
| Mobile phase A | ACN/water/acetic acid (60/40/0.02, v/v) |
| Mobile phase B | ACN/isopropanol (50/50, v/v) |
| Gradient | 0–4.0 min: 0.1–55% B; 4.0–4.5 min: 55–99% B; 4.5–5.0 min: 99% B |
We use scheduled MRM to maintain sensitivity while supporting multi-analyte panels.
| Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Ionization mode | ESI negative |
| Acquisition mode | Scheduled MRM |
| Scheduling window | 30 s per transition |
| Curtain gas (CUR) | 10 psi |
| Gas 1 (GS1) | 30 psi |
| Gas 2 (GS2) | 30 psi |
| Ion spray voltage | −4.5 kV |
| Source temperature | 525 °C |
| Collision gas | Nitrogen (CID optimized per analyte) |

Waters ACQUITY UPLC System (Figure from Waters)

SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ (Figure from Sciex)
Explore our Lipidomics Solutions brochure to learn more about our comprehensive lipidomics analysis platform.

Inflammatory stimulation kinetics
Track rapid eicosanoid synthesis changes across COX/LOX/CYP after LPS/cytokine or stress perturbations.

Mechanism-of-action and PD readouts
Quantify pathway outputs to confirm target engagement or pathway rerouting in inhibitor/agonist studies.

Tumor microenvironment research
Profile prostaglandins/leukotrienes/HETEs to connect lipid mediators with immune and inflammatory phenotypes in models.

Metabolism and nutrition interventions
Measure how omega-3/omega-6 inputs reshape downstream mediator patterns in controlled designs.

Oxidative stress models
Separate enzymatic eicosanoid changes from oxidation-linked signatures under defined stress conditions.

Genetics and pathway engineering
Compare eicosanoid pathway outputs across KO/KD/overexpression systems to validate branch dependencies.
| Matrix | Typical minimum | Container and handling notes |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma / serum | 200–500 μL | Use pre-chilled polypropylene; keep cold; avoid repeated freeze–thaw |
| Urine | 1–2 mL | Clarify, aliquot, and freeze; normalization strategy can be discussed |
| CSF | ~200 μL | Use low-bind tubes when possible; freeze quickly |
| Tissue | 30–100 mg | Snap-freeze; record wet weight; avoid thaw cycles |
| Cell pellets | ≥1×106 cells | Cold washes; snap-freeze; provide cell count metadata |
| Culture media | 1–2 mL | Clarify and freeze; note serum supplementation |
Collection, Storage, and Shipping
How do you separate eicosanoid isomers (e.g., 5-HETE vs 12-HETE)?
We use Waters ACQUITY UPLC with BEH Shield RP18 chemistry to improve chromatographic resolution for structural isomers with similar MS/MS behavior. Separation is confirmed by retention time (RT) and qualifier/quantifier consistency before quantitation.
Why use isotope dilution for eicosanoid quantification?
Eicosanoids are prone to ESI matrix effects. We apply isotope dilution with 26+ deuterated internal standards spiked pre-extraction to correct recovery loss and ionization variability, improving quantitative reliability in complex matrices.
How do you reduce ex vivo oxidation and artifacts?
We follow a stability-focused handling plan: rapid processing, cold-chain control, and project-appropriate stabilization steps to minimize enzymatic activity and non-enzymatic oxidation during collection and storage.
Can you report results by COX/LOX/CYP pathways?
Yes. Outputs can be organized into COX, LOX, and CYP sub-panels to support pathway-level interpretation and mechanism studies.
Why use LC–MS/MS instead of ELISA for eicosanoids?
LC–MS/MS improves chemical specificity and supports multiplex measurement, reducing cross-reactivity risk that can affect antibody-based assays.
What's the difference between eicosanoids and oxylipins?
Oxylipins are a broad class of oxidized polyunsaturated fatty acid mediators. Eicosanoids are a major subset of oxylipins, typically derived from 20-carbon fatty acids such as arachidonic acid, and include prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, and related products.
Can you normalize eicosanoids in cell culture supernatants?
Yes. We can report results normalized to cell count, total protein, or other study-defined metadata you provide.
Are eicosanoids hormones?
Eicosanoids are often described as hormone-like local mediators (autacoids). They act near their site of production and change rapidly with pathway activity, which is why targeted LC–MS/MS is commonly used to quantify them in research models.

Services:
Resource:
Platform:
Online Inquiry
CONTACT US