Full-Spectrum Free Fatty Acid Profiling
Simultaneous detection of 50+ FFAs (C6–C24) across biological and food samples using LC-MS/MS and GC-MS platforms
Our services have earned the trust of companies, schools, and organizations globally, and we remain dedicated to maintaining that trust.
Free fatty acids (FFAs) are a crucial class of lipid molecules that exist unbound in biological systems. Structurally, FFAs consist of a hydrocarbon chain terminating in a carboxyl functional group, which determines their chemical properties and metabolic roles. These fatty acids play a central role in cellular energy metabolism, serving as vital fuel sources. Additionally, they contribute to various physiological processes, including membrane biosynthesis, signaling pathways, and lipid homeostasis.
Full-Spectrum Free Fatty Acid Profiling
Simultaneous detection of 50+ FFAs (C6–C24) across biological and food samples using LC-MS/MS and GC-MS platforms
Free Fatty Acid Absolute Quantification
Trace-level quantification (detection limit: 0.6 μM) with isotope-labeled internal standards for precision
Customized Free Fatty Acid Panels
Targeted analysis of specific FFAs (e.g., palmitic, oleic, linoleic acids) or pathway-focused panels (e.g., β-oxidation intermediates)
Multi-Omics Integration Analysis
Combine FFA data with proteomics or metabolomics for holistic insights into lipid metabolism
Saturated fatty acids contain no double bonds in their hydrocarbon chains. They play critical roles in energy storage and membrane structure.
| Compound | Chain Length | Related Metabolites | Metabolic Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Palmitic Acid (C16:0) | 16 | Palmitoyl-CoA, Acetyl-CoA | β-Oxidation, Lipogenesis |
| Stearic Acid (C18:0) | 18 | Stearoyl-CoA, Acetyl-CoA | β-Oxidation, Lipogenesis |
| Myristic Acid (C14:0) | 14 | Myristoyl-CoA | β-Oxidation, Protein Modification |
| Lauric Acid (C12:0) | 12 | Dodecanoyl-CoA | β-Oxidation, Lipogenesis |
Monounsaturated fatty acids contain one double bond, contributing to membrane fluidity and cellular signaling.
| Compound | Chain Length | Related Metabolites | Metabolic Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oleic Acid (C18:1) | 18 | Oleoyl-CoA, Hydroxyoleic Acid | Lipid Signaling, Lipogenesis |
| Palmitoleic Acid (C16:1) | 16 | Palmitoleoyl-CoA, Acetyl-CoA | β-Oxidation, Fatty Acid Desaturation |
| Vaccenic Acid (C18:1) | 18 | Vaccenoyl-CoA | Lipid Signaling, Energy Metabolism |
Polyunsaturated fatty acids contain multiple double bonds and are essential for inflammatory response, brain function, and hormone production.
| Compound | Chain Length | Related Metabolites | Metabolic Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linoleic Acid (C18:2) | 18 | Arachidonic Acid, Eicosanoids | Eicosanoid Synthesis, Lipogenesis |
| Arachidonic Acid (C20:4) | 20 | Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes | Inflammatory Response, Cell Signaling |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid (C22:6) | 22 | DHA-Derived Mediators | Neuroprotection, Lipid Signaling |
| Eicosapentaenoic Acid (C20:5) | 20 | Resolvins, Protectins | Anti-Inflammatory Pathways |
Hydroxylated fatty acids have hydroxyl (-OH) groups, contributing to lipid signaling and metabolic regulation.
| Compound | Chain Length | Related Metabolites | Metabolic Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid (C4:0) | 4 | Acetoacetate, Acetyl-CoA | Ketogenesis, Energy Metabolism |
| 12-Hydroxystearic Acid (C18:0) | 18 | Hydroxyoctadecanoic Acid | Lipid Signaling, Inflammatory Response |
Branched-chain fatty acids have methyl branches, often derived from microbial metabolism and are detected in dairy and meat products.
| Compound | Chain Length | Related Metabolites | Metabolic Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phytanic Acid (C20:0) | 20 | Pristanic Acid, Acetyl-CoA | α-Oxidation, Peroxisomal Metabolism |
| Pristanic Acid (C19:0) | 19 | Acyl-CoA, Propionyl-CoA | β-Oxidation, Energy Metabolism |
Instrument: Agilent 7890B GC System coupled with Agilent 5977B MSD
Instrument: Thermo Fisher Scientific Q Exactive™ Plus Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap™ Mass Spectrometer
Instrument: Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC System
Results we provide:
Format:
Contents:
Format:
Contents:
Format:
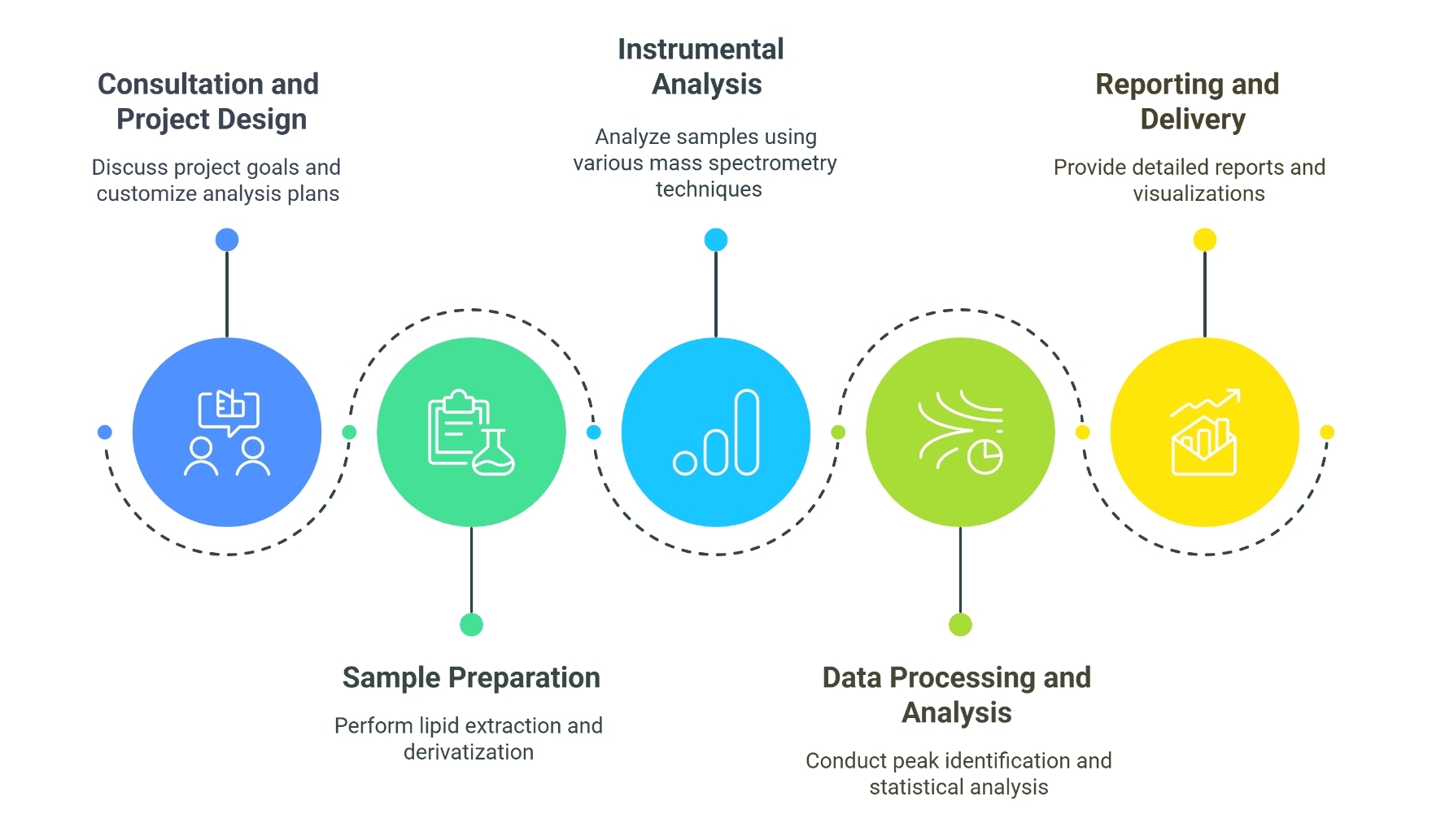
 Workflow of Lipidome Data Analysis
Workflow of Lipidome Data Analysis
Explore our Lipidomics Solutions brochure to learn more about our comprehensive lipidomics analysis platform.

Metabolic Research
Investigate the role of free fatty acids in cellular energy metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, and biochemical pathway regulation.
Biotechnology Development
Optimize lipid production in microbial strains for biofuel, bioplastic, and other bio-based material applications.

Agricultural Studies
Analyze plant lipids, soil fatty acids, and microbial communities to monitor soil health, crop quality, and agricultural productivity.

Environmental Monitoring
Track changes in fatty acid profiles as biomarkers for pollution exposure, microbial activity, and ecosystem health assessments.
Nutritional Research
Evaluate the fatty acid composition of foods, oils, and dietary supplements to assess nutritional value and lipid quality.

Food Quality and Safety
Monitor fatty acid composition, detect lipid oxidation, and ensure product stability during food processing, storage, and distribution.
| Sample Type | Required Amount | Storage Conditions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | ≥ 200 µL | -80°C | Avoid hemolysis; use EDTA or heparin tubes. |
| Serum | ≥ 200 µL | -80°C | Allow complete clotting before centrifugation; remove lipemic samples if possible. |
| Tissue | ≥ 50 mg | -80°C | Flash freeze in liquid nitrogen; store in cryotubes. |
| Cell Culture | ≥ 1 × 10⁶ cells | -80°C | Wash cells with PBS, pellet cells, and freeze immediately. |
| Urine | ≥ 500 µL | -80°C | Collect midstream urine and store without preservatives. |
| Feces | ≥ 100 mg | -80°C | Ensure minimal exposure to air; freeze promptly. |
| Plant Samples | ≥ 100 mg | -80°C | Freeze immediately and store in sealed containers to prevent lipid oxidation. |
| Food and Oil Samples | ≥ 1 g or 1 mL | 4°C or -20°C | Store in dark, airtight containers to avoid oxidation. |
| Microbial Cultures | ≥ 1 × 10⁹ cells or equivalent | -80°C | Pellet cultures by centrifugation and wash with PBS before freezing. |
How should biological samples (e.g., plasma, tissues) be collected to ensure FFA stability?
Critical Steps:
What are the best practices for handling lipid-rich samples (e.g., oils, dairy products)?
Contamination Control:
Oxidation Prevention: Add antioxidants (e.g., 0.01% BHT) during extraction and perform steps under nitrogen/argon atmosphere .
How do I optimize FFA extraction for complex matrices like sewage sludge or microbial cultures?
Specialized Protocols:
What are the QA/QC measures to ensure FFA quantification accuracy?
Can I analyze FFAs in small-volume or non-invasive samples (e.g., dried blood spots)?
How do I design experiments for metabolic flux or lipid oxidation studies?
What are the industry-specific considerations for FFA analysis?

References
Services:
Resource:
Platform:
Online Inquiry
CONTACT US