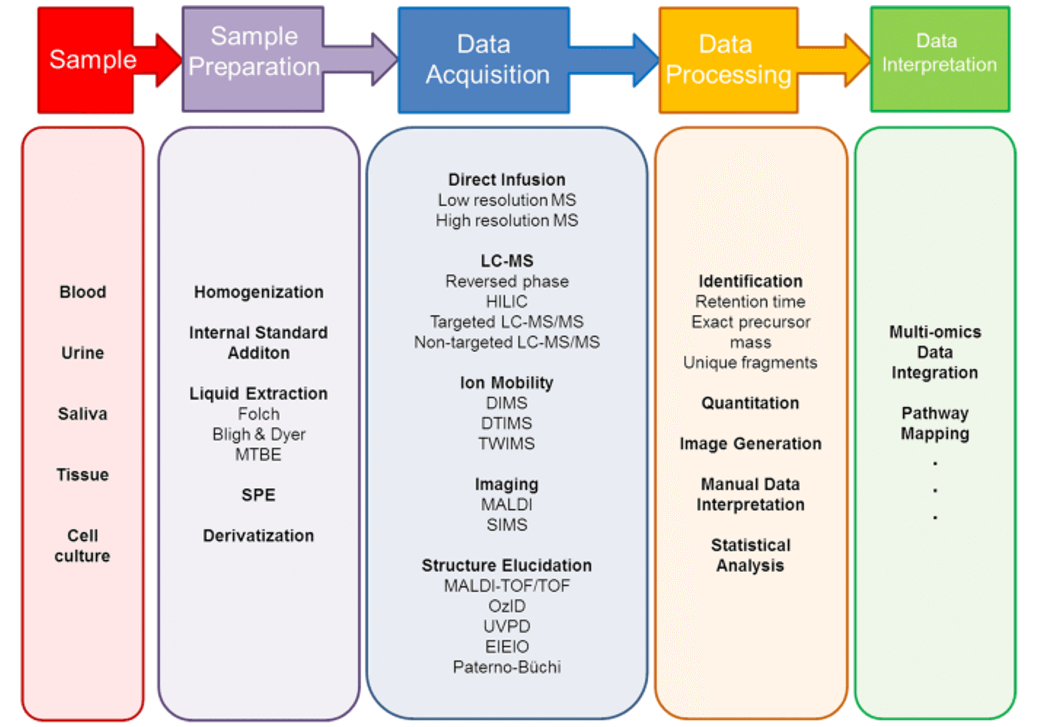
Human Milk Lipidomics and Other Mammalian Lipidomics
The lipid fraction only accounts for 5% of the total components of human milk, but the lipids in human milk are very important for babies. They are not only the main source of energy for the growth of babies, but also play a role in immune interaction and service. In addition, it is also related to infant nerve and retinal development.
The lipid group of human milk is complex. Lipids are strategically packaged as milk fat globules (MFG). MFG wraps triglycerides (TAGs) in the core, accounting for 98-99% of the total human milk lipid group. The surrounding MFG membrane is composed of other more polar lipids, such as cholesterol and phospholipids.
The content of total lipids in human milk varies greatly, during the day, between breasts, between women, and throughout the lactation period.
With the variability of human milk lipids, the complexity and lipid hydrophobicity of the milk matrix increase the difficulty of comprehensive lipidomics analysis.
Creative Proteomics provides reliable, rapid and cost-effective human milk untargeted lipidomics with GC/LC-QTOF-MS, which has the capacity to differentiate isomeric TAGs based on their structural arrangements and potentially identify more individual TAGs at once, as has been achieved for other lipid species. We also offer other mammals milk untargeted lipidomics services, including cow, macaque, goats, yaks, and pigs.
Milk Lipidomics Service in Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics is based on the liquid-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) unbiased detection of all lipid molecules in milk samples as much as possible. We use statistical analysis to screen differential lipid molecules, discover the relative relationship between lipid metabolism changes and physiological and pathological changes, and reveal the mechanism of lipids in various life activities.
Sample Preparation and Extraction
Accurate and reliable analysis of human milk lipids begins with meticulous sample preparation and extraction. Creative Proteomics employs standardized protocols to ensure reproducibility and minimize variation. Lipid extraction techniques, such as liquid-liquid extraction or solid-phase extraction, are carefully selected based on the sample volume and the specific research objectives.
Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Creative Proteomics utilizes high-resolution mass spectrometry, such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), for lipid profiling. LC-MS offers exceptional sensitivity and selectivity, enabling the detection and quantification of a wide range of lipid species in human milk samples.
The acquired data undergoes thorough processing, including peak alignment, normalization, and deconvolution, to ensure accurate identification and quantification of lipids. Advanced data analysis software enables the generation of lipid profiles, hierarchical clustering, and statistical analyses to uncover meaningful patterns and associations within the data.
Lipid Identification and Quantification
By leveraging comprehensive lipid databases and advanced algorithms, the service accurately annotates the detected lipid species. The relative abundance of individual lipids across samples is quantified, facilitating comparisons between different milk samples or within the same sample across different lactation stages.
Data Interpretation and Integration
The acquired lipidomics data is processed and analyzed using sophisticated software tools. This includes peak alignment, normalization, and deconvolution techniques to ensure accurate identification and quantification of lipid species. By leveraging comprehensive lipid databases and advanced algorithms, the service annotates and quantifies the detected lipid species. The relative abundance of individual lipids across samples is determined, enabling comparisons between different milk samples or within the same sample across different lactation stages.
We employ a range of statistical methods to identify significant differences in lipid profiles and explore associations between lipids and various factors, such as maternal characteristics or dietary intake. These statistical analyses help identify lipid species that are significantly altered under different conditions, providing insights into the factors that influence human milk lipid composition.
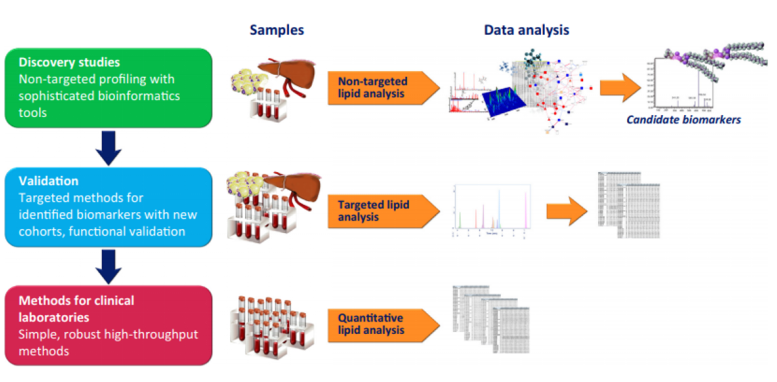
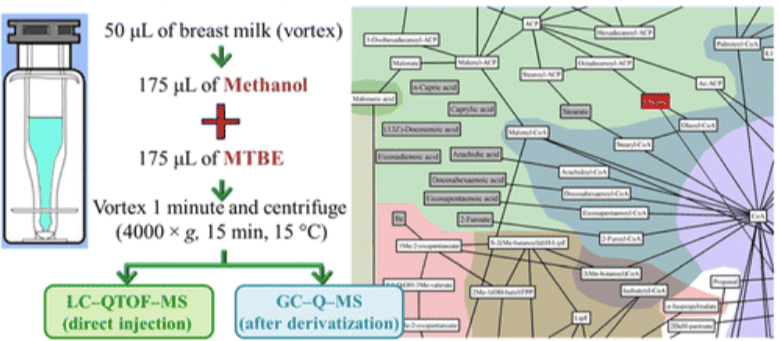 Fig 1. The workflow of milk untargeted lipidomics. (Villaseñor, A et al., 2014)
Fig 1. The workflow of milk untargeted lipidomics. (Villaseñor, A et al., 2014)
Sample Requirements of Milk Lipidomics
Sample Types
- Human Milk: The service specializes in the analysis of human milk samples, including colostrum, transitional milk, and mature milk.
- Animal Milk: Certain animal milk samples, such as cow's milk or goat's milk, may also be accepted. Please consult with Creative Proteomics to confirm the suitability of specific animal milk samples.
Suggested Sample Volumes
- Human Milk: A minimum volume of 10 mL is recommended for human milk samples. However, providing larger volumes is preferred to ensure an ample lipid content for comprehensive analysis.
- Animal Milk: The sample volume requirements for animal milk may vary. It is advisable to consult with Creative Proteomics regarding the specific volume recommendations for animal milk samples.
It is crucial to handle, store, and prepare the milk samples correctly to preserve the integrity of the lipid composition. Follow the guidelines below:
Sample Handling and Storage
- Collection: Use sterile containers during sample collection to minimize contamination. Ensure that the samples are not exposed to excessive light, heat, or agitation.
- Storage Temperature: Immediately after collection, store the milk samples at -80°C or below to maintain the lipid composition. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles, as they can lead to lipid degradation.
- Container Selection: Choose suitable storage containers, such as cryovials or polypropylene tubes, to prevent lipid adsorption or leaching from the container walls.
- Sample Labeling: Clearly label each sample container with unique identifiers, including sample ID, lactation stage, and any other relevant information for proper documentation and traceability.
Why Choose Creative Proteomics for Milk Lipidomics Analysis?
State-of-the-Art Mass Spectrometry
Creative Proteomics utilizes cutting-edge mass spectrometry platforms for milk lipidomics analysis. Our instruments include high-resolution mass spectrometers with accurate mass capabilities, such as Orbitrap and Q-TOF systems. These advanced platforms enable precise and sensitive analysis of a wide range of milk lipid species, including fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and sphingolipids.
Quantitative Profiling of Milk Lipids
Our expertise lies in comprehensive quantitative profiling of milk lipids. We employ targeted and untargeted lipidomics approaches to identify and quantify specific lipid classes and individual lipid species in milk samples. Our methods encompass both shotgun lipidomics and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) techniques, allowing for in-depth analysis of the lipidome with high accuracy and reproducibility.
High-Throughput Analysis
At Creative Proteomics, we understand the importance of efficiency in research projects. Our state-of-the-art instrumentation, combined with automated sample handling systems, enables high-throughput analysis of milk lipidomics samples. This capability allows for rapid turnaround times, making our service ideal for projects with large sample cohorts or time-sensitive research objectives.
Advanced Data Analysis and Interpretation
We offer comprehensive data analysis and interpretation services to extract meaningful insights from the complex milk lipidomic datasets. Our bioinformatics experts employ advanced statistical algorithms, multivariate analysis, and pathway analysis tools to identify significant lipidomic changes and understand the functional implications. We provide detailed reports, visualizations, and customized data interpretation to facilitate a deeper understanding of the milk lipid composition.
Quality Assurance and Standardization
Rigorous quality control is applied throughout the analytical process to ensure accurate and reliable results. Comprehensive quality management practices, including thorough documentation and traceability, are maintained. Participation in proficiency testing programs supports ongoing evaluation and improvement of analytical performance.
Customized Experimental Design
We recognize that each research project has unique requirements. Our team of experts collaborates closely with clients to understand their specific research goals and design customized experimental protocols. This tailored approach ensures that the milk lipidomics analysis aligns with the objectives of the project, maximizing the relevance and usefulness of the obtained results.
Data Security and Confidentiality
We prioritize data security and maintain strict confidentiality throughout the analysis process. Our infrastructure includes secure data management systems, encrypted communication channels, and stringent access controls to safeguard client data. We sign non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) to ensure the confidentiality of project-specific information, protecting the intellectual property and sensitive data of our clients.
Why Choose Us?
- Fast turnaround time: 1-4 weeks.
- Bioinformatics service: data processing (e.g., data alignment, feature detection), feature prioritization (e.g., principal component analysis, heat maps, ANOVA/t-test, multivariate statistical analysis, self organizing maps, volcano plots, and network activity prediction), and lipid identification services.
- Detailed delivery report: Experiment procedures and parameters of instruments, MS data with putative identification based on the m/z ratio of the analytes, and customized bioinformatics analysis.
If you have any questions about our milk lipidomics service, please contact us.
References:
- Villaseñor, A.; et al. Breast Milk Metabolome Characterization in a Single-Phase Extraction, Multiplatform Analytical Approach. Analytical Chemistry. 2014, 86, 8245-8252.
- George, A.D.; et al. Untargeted lipidomics using liquid chromatography-ion mobility-mass spectrometry reveals novel triacylglycerides in human milk. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 9255.
* Our services can only be used for research purposes and Not for clinical use.
Services:
Resource:
Platform:


 Fig 1. The workflow of milk untargeted lipidomics. (Villaseñor, A et al., 2014)
Fig 1. The workflow of milk untargeted lipidomics. (Villaseñor, A et al., 2014)