Bacterial Lipidomics Service
Lipids are one of the major components of food, and also, they are important components of cellular biofilms and building blocks. In addition, lipids can be used for energy storage and metabolism and are signaling molecules for many cellular activities. Thus, the regulation of lipid metabolism is essential for maintaining homeostasis. The lipids found in bacteria may be very different from those found in eukaryotic systems, but they are equally important for maintaining the structure of bacteria and providing protection against their surroundings.
Biofilms are heterogeneous aggregates composed of a combination of surface-attached microorganisms and the biomacromolecular polymorphic matrix they produce that is wrapped around the surface. A wide range of pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms are capable of producing biofilms. Lipidomics can be used to study the regulatory mechanisms affecting bacterial biofilm formation. The structure of the envelope and the enrichment of diverse and functionally important lipids can help to differentiate bacteria. And envelope lipids may also be involved in biofilm formation.
Lipid metabolism includes both lipid anabolism and lipid catabolism. Studying bacterial lipid metabolism can help accelerate scientific research progress related to bacterial infection mechanisms and disease prevention, control and treatment. For example, lipid synthesis in Mycobacterium is essential for maintaining cell wall stability and is often used as a target for the development of anti-tuberculosis drugs. Mycobacterium bovis lipid catabolism plays an important role in the maintenance of host intracellular survival by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Studying the regulation of lipid metabolism in Mycobacterium bovis will provide important clues for the prevention, control and treatment of tuberculosis. Host lipid metabolism as well as obesity can be improved by regulating the intestinal flora. Intestinal bacteria can translocate across the mucosa to colonize mesenteric lipids, blood, and other distal tissues and participate in physiological metabolic countermeasures. With the help of lipidomics can provide new ideas for the study of microbial and lipid metabolism interactions.
Depending on the research objectives, Creative Proteomics offers you different strategies for lipidomics analysis. Take a targeted lipidomic analysis, which analyzes only specific lipids to cover specific pathways, or possibly take an untargeted lipidomic approach, which aims to detect a large number of lipid species to gain system-level insight.
Our Bacterial Lipidomics Service
We have a complete technology platform for identification and quantification of bacterial lipidomics, including GC-FID, GC-MS and LC-MS. Data analysis includes PCA, PLS-DA, PLS-R and univariate statistics. Generate a lipid list and classify the data based on the selected statistical test (f-test, t-test or regression and export list) for further analysis, such as enrichment and KEGG pathway analysis.
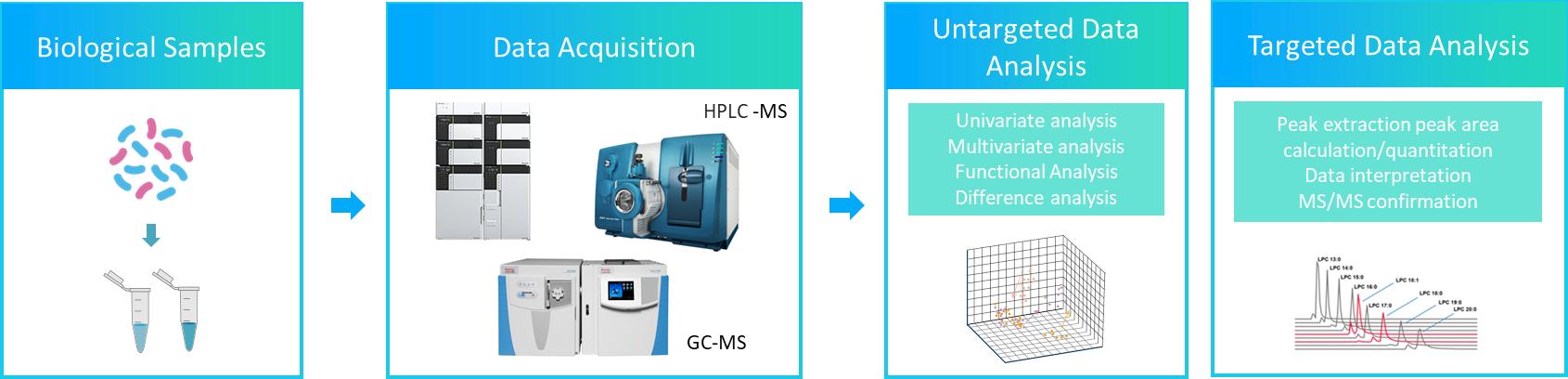 Fig1. The workflow of bacterial lipidomics service.
Fig1. The workflow of bacterial lipidomics service.
Why Choose Us?
- One-stop services from prepare the samples, run the mass spectrometric analysis, process the data, perform statistical analysis, and identify the compounds.
- Provides a comprehensive visual report of the results. The report will help to answer your study questions, and hopefully create a few new ones to follow.
- Visualize data results and provide actionable advice on how to leverage them in your research or business.
If you have any questions about our bacterial lipidomics services, please contact us.
* Our services can only be used for research purposes and Not for clinical use.
Services:


 Fig1. The workflow of bacterial lipidomics service.
Fig1. The workflow of bacterial lipidomics service.