Lipidomics in Skin Diseases
Skin is the largest organ serving multiple functions in the mammalian body, mainly providing a barrier that protects the body against external irritation and infections as well as preventing water loss. The skin is composed of the epidermis, dermis and subcutis. The epidermis, the exterior of the skin, mainly consists of four distinctive cell layers: the stratum basale (SB), the stratum spinosum (SS), the stratum granulosum (SG) and the stratum corneum (SC). The outmost layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum (SC), is comprised of large, flattened, enucleated corneocytes and a lipid-enriched extracellular matrix. The SC is often referred to as a "bricks in mortar" structure, in which corneocytes act as the bricks and the lipids act as the mortar, and it plays a critical role in skin permeability barrier formation and maintenance. The presence of intercellular lipids is essential for the maintenance of a moist, pliable and healthy skin barrier. Alteration of SC lipids composition leads to disrupted or impaired skin barrier functions and results in an increase in transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
The application of lipidomics in the study of skin biology and inflammatory skin diseases has attracted particular attention. Several studies have suggested that alterations in lipid composition may play an important role in skin barrier impairment, which is a major cause of some inflammatory skin diseases.
Creative Proteomics has a high-sensitivity and high-resolution UPLC-MS instrument that enables multivariate analysis of lipid and metabolic changes, characterizing changes in the profile of lipid compounds and identifying significantly altered lipid analogs.
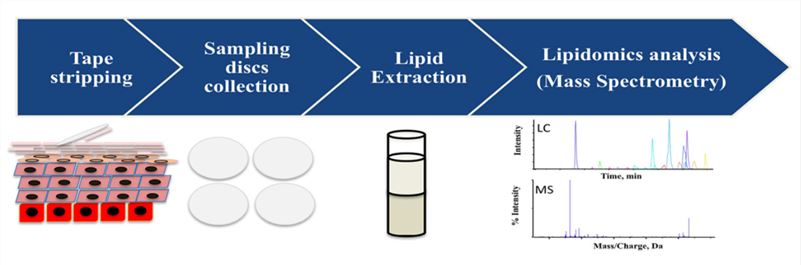 Fig1. A typical lipidomics analysis workflow on a human SC sample (Li, Shan.; et al, 2016)
Fig1. A typical lipidomics analysis workflow on a human SC sample (Li, Shan.; et al, 2016)
Featured Services
Strategies for Lipidomic Analysis of Skin Diseases
Creative Proteomics designs experimental programs according to customer needs and chooses different technical methods to improve detection efficiency and ensure the accuracy and repeatability of experimental results.
Based on LC-MS/MS technology to simultaneously analyze hundreds of different lipids in biological samples to obtain more information. Through bioinformatics data analysis, we can systematically elucidate the variation at the lipidome level and the regulatory mechanisms in the experimental group compared to the control group from a lipid perspective.
Targeting specific lipid molecules and their metabolites in samples. Based on high-resolution mass spectrometry and isotope internal standard, we use parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) targeted analysis technology, which can realize the specific acquisition of signals of multiple lipid molecules (such as dozens of target lipid molecules) at the same time, and obtain their absolute contents to meet the needs of targeted detection and verification of target lipids. Using Orbitrap mass analyzer and ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry, high quality data can be obtained. Sensitivity up to ppm level and linearity range up to 5-6 orders of magnitude.
Case
Atopic dermatitis is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by disrupted epidermal barrier functions. About 15%–20% of children and 1–3% of adults are affected by AD.
A study performed lipidomics analysis using normal-phase liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry to compare the SC CERs profile between AD patients and healthy individuals within small groups. The study showed that the level of total CERs as well as those of the CERNH], CERNP], CEREOS], CEREOH], and CEREOP] classes were significantly lower in AD lesional skin compared with controlled healthy non-lesional skin[45]. In addition, the levels of certain CER species with short chain lengths (e.g. CERNS], CERNDS], CERAS]) were lower in AD patients and certain CER species with long chain lengths (e.g. CERNS], CERNDS], CERNH], CERAS], CERAH] were significantly higher in AD subjects.
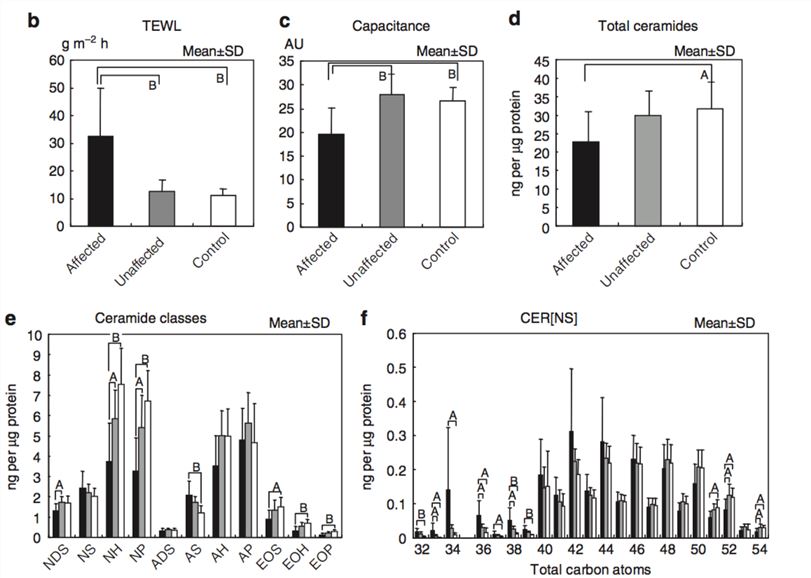 Fig2. Ceramide profiles in AD patients and healthy subjects (Persikov, A. V.; et al 2010)
Fig2. Ceramide profiles in AD patients and healthy subjects (Persikov, A. V.; et al 2010)
With decades of operational experience and technology platform, Creative Proteomics provides reliable, rapid, and cost-effective plant lipidomics services based on LC-MS methods for skin diseases research.
How we work in 7 easy steps

With decades of operational experience and technology platform, Creative Proteomics provides reliable, rapid, and cost-effective lipidomics solutions for skin diseases research. If you have any question for skin diseases research, please contact us. We look forward to working with you in the future.
References:
- Li, Shan.; et al. Lipidomic analysis of epidermal lipids: a tool to predict progression of inflammatory skin disease in humans. Expert review of proteomics. 2016, 13.5 (2016): 451-456.
- Persikov, A. V.; et al. Changes in the ceramide profile of atopic dermatitis patients. J Invest Dermatol. 2010, 130: 2511-4.
* Our services can only be used for research purposes and Not for clinical use.
Applications:


 Fig1. A typical lipidomics analysis workflow on a human SC sample (Li, Shan.; et al, 2016)
Fig1. A typical lipidomics analysis workflow on a human SC sample (Li, Shan.; et al, 2016) Fig2. Ceramide profiles in AD patients and healthy subjects (Persikov, A. V.; et al 2010)
Fig2. Ceramide profiles in AD patients and healthy subjects (Persikov, A. V.; et al 2010)