Lipidomics in Nutrition and Health
Disorders or abnormalities of lipid metabolism may lead to the development of many human diseases. For example, obesity, a disease caused by an imbalance between calorie intake and consumption, has become a common problem in many developed countries, and obese people are at considerable risk for cardiovascular disease and diabetes. The diseases caused by lipid metabolism go far beyond this, so it is important to apply the study of lipid metabolism of specific molecular species to nutrition.
With the introduction of high-throughput and high-precision lipidomic analysis methods, lipid species, structure, function and their metabolic regulatory networks have been studied in depth, thus better revealing the relationship between lipids and the nutrition and health of living organisms.
Based on chromatography-mass spectrometry, lipidomics is a powerful platform to study the overall lipid profile in biological systems. Changes in circulating lipids in response to dietary interventions can be monitored, and relationships between diet and lipid metabolism can be established.
Creative Proteomics offers lipidomics solutions for nutrition and health research to help elucidate how ingested food components contribute to health and disease at the molecular level.
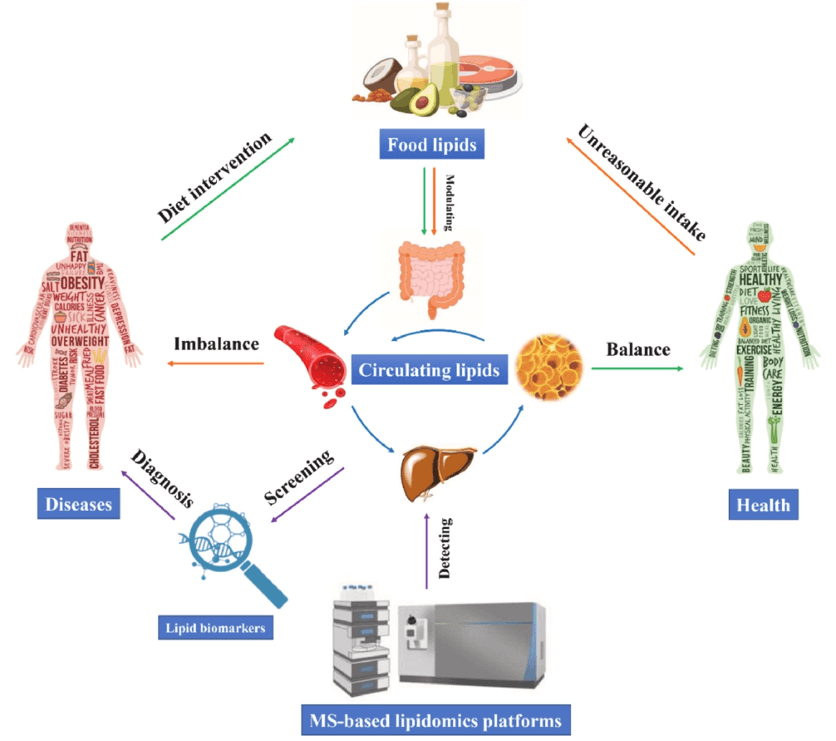 Fig1. The role of lipidomics in revealing the relationships between dietary lipids and health status (Wu, Bangfu.; et al, 2020)
Fig1. The role of lipidomics in revealing the relationships between dietary lipids and health status (Wu, Bangfu.; et al, 2020)
Case
Fish consumption has been correlated with benefits against cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, among others. But the physiological mechanisms remain unclear and the health benefit varies with the diversity of fish consumption. A study has investigated the serum lipidomic profiles in subjects with coronary heart disease after an 8-week diet intervention with fatty fish or lean fish.
Over 300 lipids were identified and quantified by the UPLC-MS lipidomics platform. Among them, multiple lipids including Cer, LPC, DAG, PC, LPE and cholesterol ester (CE) decreased significantly in the fatty fish group when compared to control group and lean fish group. Cer, LPC, DAG are potential mediators of lipid-induced insulin resistance and inflammation. Therefore, the study indicated that the consumption of fatty fish would lead to a protective effect on the progression of coronary heart disease.
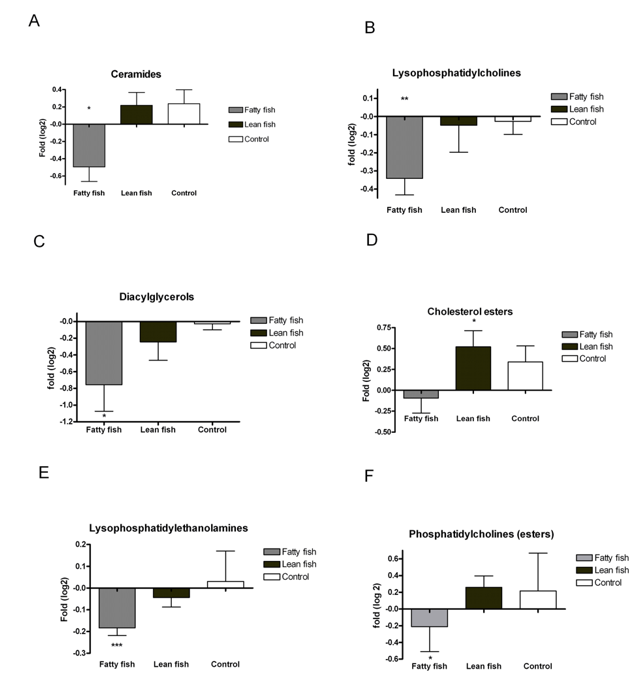 Fig2. Bar charts of fold changes for different lipid classes (Lankinen, Maria.; et al, 2009)
Fig2. Bar charts of fold changes for different lipid classes (Lankinen, Maria.; et al, 2009)
Therefore, unreasonable intake of food lipids will lead to the imbalance of circulating lipids that result in diseases or disorders and, conversely, some diseases can be prevented, alleviated or even cured through dietary lipids intervention. MS-based lipidomics platforms can be employed for lipid biomarkers discovery to monitor the development or predict the upcoming of many diseases. Creative Proteomics provides comprehensive lipidomics services from lipid extraction, lipid detection, and data analysis for nutrition and health research.
Related Featured Services
How we work in 7 easy steps

If you have any questions about our lipidomics services in nutrition and health research, please contact us. With our highly experienced scientific team, advanced techniques and equipment, we are able to tailor our services according to your needs.
References:
- Wu, Bangfu.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based lipidomics as a powerful platform in foodomics research. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2020.
- Lankinen, Maria.; et al. Fatty fish intake decreases lipids related to inflammation and insulin signaling—a lipidomics approach. PLoS one. 2009, 4.4: e5258.
* Our services can only be used for research purposes and Not for clinical use.


 Fig1. The role of lipidomics in revealing the relationships between dietary lipids and health status (Wu, Bangfu.; et al, 2020)
Fig1. The role of lipidomics in revealing the relationships between dietary lipids and health status (Wu, Bangfu.; et al, 2020) Fig2. Bar charts of fold changes for different lipid classes (Lankinen, Maria.; et al, 2009)
Fig2. Bar charts of fold changes for different lipid classes (Lankinen, Maria.; et al, 2009)